


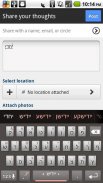
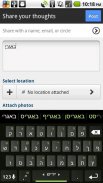
Yiddish Keyboard Plugin

Yiddish Keyboard Plugin açıklaması
Yiddish Dictionary plugin for Multiling O Keyboard autocorrect and word prediction
Instruction:
⑴ Install this plugin and Multiling O Keyboard. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=kl.ime.oh
⑵ Run O Keyboard and follow its setup guide.
⑶ Slide space bar to switch languages.
If you have font issue, read this: <a href="https://www.google.com/url?q=https://www.google.com/url?q%3Dhttp://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html%26sa%3DD%26usg%3DAFQjCNG71Nl5i6QMcdEZvU1BqM2L70OWlQ&sa=D&usg=AFQjCNHJAfktVVilzCrduIwvK96EQvYRGw" target="_blank">http://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html</a>
Wikipedia:
Yiddish (ייִדיש, יידיש or אידיש, yidish/idish, literally "Jewish") is the historical language of the Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the pre-existing language of the nascent Ashkenazi community with an extensive Germanic based vocabulary. Yiddish is written with a fully vocalized alphabet based on the Hebrew script.
The earliest surviving references date from the 12th century and call the language לשון־אַשכּנז (loshn-ashknez = "language of Ashkenaz") or טײַטש (taytsh), a variant of tiutsch, the contemporary name for Middle High German. In common usage, the language is called מאַמע־לשון (mame-loshn, literally "mother tongue"), distinguishing it from Hebrew and Aramaic, which are collectively termed לשון־קודש (loshn-koydesh, "holy tongue"). The term "Yiddish" did not become the most frequently used designation in the literature until the 18th century. In the late 19th and into the 20th century the language was more commonly called "Jewish", especially in non-Jewish contexts, but "Yiddish" is again the more common designation.
Modern Yiddish has two major forms. Eastern Yiddish is far more common today. It includes Southeastern (Ukrainian–Romanian), Mideastern (Polish–Galician–Eastern Hungarian), and Northeastern (Lithuanian–Belarusian) dialects. Eastern Yiddish differs from Western both by its far greater size and by the extensive inclusion of words of Slavic origin. Western Yiddish is divided into Southwestern (Swiss–Alsatian–Southern German), Midwestern (Central German), and Northwestern (Netherlandic–Northern German) dialects. Yiddish is used in a large number of Orthodox Jewish communities worldwide and is the first language of the home, school, and in many social settings among most Hasids. Yiddish is also the academic language of the study of the Talmud according to the tradition of the Lithuanian yeshivas.
The term Yiddish is also used in the adjectival sense, synonymously with Jewish, to designate attributes of Ashkenazi culture (for example, Yiddish cooking and Yiddish music).[4]
</div> <div jsname="WJz9Hc" style="display:none">Multiling O Klavye Otomatik Düzelt ve kelime tahmini için Yidiş sözlük eklentisi
Talimat:
Bu eklentiyi ve Multiling O Klavye yükleyin ⑴. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=kl.ime.oh
⑵ çalıştırın O Klavye ve kurulum kılavuzu izleyin.
⑶ Slayt space bar dilleri geçmek için.
Yazı tipi sorunu varsa, bu okuyun: <a href="https://www.google.com/url?q=http://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html&sa=D&usg=AFQjCNG71Nl5i6QMcdEZvU1BqM2L70OWlQ" target="_blank">http://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html</a>
Vikipedi:
Yidiş (ייִדיש, יידיש veya אידיש, yidish / idish, kelimenin tam anlamıyla "Yahudi") Aşkenaz Yahudilerinin tarihi dilidir. Geniş bir Germen tabanlı kelime ile doğmakta olan Aşkenazi topluluğunun önceden varolan dil sağlayarak, Orta Avrupa'da 9. yüzyılda ortaya çıkmıştır. Yidiş İbrani harfleriyle dayalı tam seslendirdi alfabe ile yazılmıştır.
erken kalan referansları 12. yüzyıldan bugüne ve לשון-אַשכּנז (loshn-ashknez = "Aşkenaz dili") ya da טייַטש (taytsh), tiutsch bir varyantı, Orta Yüksek Almanca çağdaş isim dilini diyoruz. Ortak kullanımda, dil denir מאַמע-לשון (mame-loshn, kelimenin tam anlamıyla "anadil"), toplu לשון-קודש (loshn-koydesh, "kutsal dil") denir İbranice ve Aramice, onu ayırt. Dönem "Yidiş" 18. yüzyıla kadar literatürde en sık kullanılan tanımı haline gelmedi. 19. yüzyıl sonu ve 20. yüzyılda dil daha yaygın, özellikle Yahudi olmayan bağlamlarda, "Yahudi" olarak adlandırılan, ancak "Yidiş" Yine daha sık atamasıdır.
Modern Yidiş iki önemli formları vardır. Doğu Yidiş bugün çok daha yaygındır. Güneydoğu (Ukrayna-Romanya), Mideastern (Lehçe-Galiçyaca-Doğu Macarca) ve Northeastern (Litvanya-Belarus) lehçeleri dahildir. Doğu Yidiş onun çok daha büyük bir boyutuna göre ve Slav kökenli sözcüklerin geniş dahil edilmesiyle hem Batı farklıdır. Batı Yidiş Güneybatı (İsviçre Almancası-Alsas-Güney), Ortabatı (Merkez Almanca) ve Northwestern (Almanca-Kuzey Netherlandic) lehçeleri ayrılmıştır. Yidiş dünya Ortodoks Yahudi cemaatlerinin çok sayıda kullanılan ve ev, okulun ilk dilidir ve en Hasids arasında birçok sosyal ortamlarda almaktadır. Yidiş ayrıca Litvanya yeşiva geleneğine göre Talmud çalışmanın akademik dilidir.
terimi Yidiş da (örneğin, Yidiş pişirme ve Yidiş müzik için) Ashkenazi kültür özelliklerini belirlemek için, eş anlamlı Musevi ile sıfat anlamda kullanılır. [4]</div> <div class="show-more-end">
























